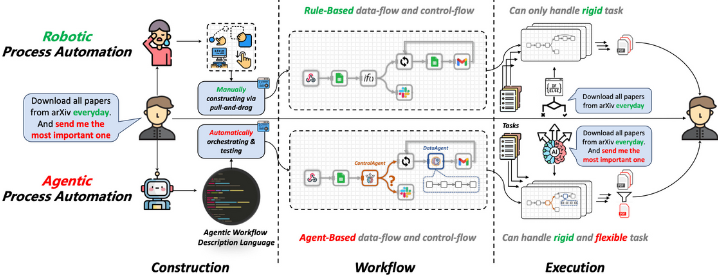
Agentic Process Automation (APA): The Next Evolution in Automation Technology
The
automation landscape is evolving at an unprecedented pace. Just as we are
becoming comfortable with robotic process automation (RPA), the industry is now
looking ahead to agentic process automation (APA) — the next wave of
intelligent automation. While RPA has transformed business processes by
automating rule-based tasks, APA promises to take things further by integrating
AI capabilities, enabling digital workers to not only execute tasks but also
make decisions, suggest improvements, and dynamically adapt to changes. Here,
we’ll explore what APA is, how it differs from RPA, its potential benefits, use
cases, and its implications for the future of work.
What is
Agentic Process Automation (APA)?
Agentic
Process Automation (APA) is an advanced form of automation that combines
AI-driven intelligence with automation capabilities. Unlike RPA, which follows
predefined instructions to perform tasks, APA incorporates large language
models (LLMs) and generative AI to enable automation systems to make decisions,
understand contexts, and even suggest process improvements. APA’s “agentic”
capabilities allow it to behave similarly to a human agent, adapting to new
situations and offering insights or improvements independently.
In
essence, APA represents a digital workforce that doesn’t just execute tasks but
also plays an active role in decision-making and problem-solving, going beyond
rule-based automation to bring more cognitive and human-like intelligence into
the fold.
Key
Differences Between APA and RPA
While RPA
and APA share the goal of streamlining business processes, their approaches
differ significantly. RPA automates repetitive, rules-based tasks, while APA
can handle complex scenarios, making autonomous decisions and adapting
workflows.
|
Feature |
Robotic
Process Automation (RPA) |
Agentic
Process Automation (APA) |
|
Task
Execution |
Executes
repetitive, rules-based tasks. |
Executes
tasks, adapts to changes, and makes context-based decisions. |
|
Context
Understanding |
Limited
to predefined steps and specific inputs. |
Interprets
situations, adapts to various inputs, and suggests actions based on context. |
|
Document
Processing |
Processes
structured documents (e.g., invoices) using fixed rules. |
Handles
various document formats, detects anomalies, and corrects them autonomously. |
|
Human
Involvement |
Requires
human intervention for exceptions or complex scenarios. |
Limited
human intervention; adapts workflows and resolves issues independently. |
|
Integration
Flexibility |
Integrates
with applications through defined APIs and workflows. |
Seamlessly
collaborates with multiple systems, interpreting and utilizing each
contextually. |
|
Decision-Making |
Follows
explicit rules; unable to self-improve or make decisions. |
Uses
AI-driven insights to make independent decisions, solve problems, and improve
tasks. |
Benefits
of Agentic Process Automation
The
integration of AI with traditional automation in APA brings a new set of
advantages that can transform how businesses operate. These benefits range from
enhanced efficiency to a more empowered human workforce.
- Increased Efficiency: APA can operate 24/7 with
minimal supervision, reducing dependency on human intervention and
decreasing the error rate. Unlike RPA, APA adapts to new data and
scenarios, improving overall productivity.
- Smarter Decision-Making: By leveraging AI, APA can
understand data, analyze patterns, and respond appropriately. This
cognitive capability allows APA to offer actionable insights, making it
suitable for processes where decision-making is essential.
- Enhanced Agility: APA excels in scenarios where
RPA encounters limitations. Its ability to understand and adapt to
unexpected situations enables greater flexibility and resilience across
workflows.
- Cost Reduction: Since APA extends automation
to more complex tasks, it can yield greater cost savings by minimizing the
need for human intervention in complex decision-making processes.
- Empowered Workforce: APA enables human employees to
focus on high-value tasks, allowing them to devote more time to
creativity, problem-solving, and strategic planning, rather than managing
repetitive tasks.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases of APA vs. RPA
To
illustrate the differences in capabilities between APA and RPA, let’s explore a
few use cases that highlight APA’s ability to handle complex tasks
autonomously.
|
Use
Case |
RPA |
APA |
|
Invoice
Processing |
Extracts
and formats invoice data for input into ERP systems; flags unrecognized
formats for review. |
Autonomously
handles discrepancies, understands diverse formats, and makes decisions
without human input. |
|
Customer
Service Chatbot |
Provides
scripted responses to FAQs; escalates complex queries to a human agent. |
Understands
customer sentiment and context, generating customized responses; continuously
learns to improve. |
|
Fraud
Detection |
Flags
unusual transactions based on fixed rules. |
Detects
complex fraud patterns, learns from evolving fraud tactics, and updates
detection criteria. |
|
Employee
Onboarding |
Follows
set onboarding workflows; requires human involvement for non-standard
scenarios. |
Customizes
workflows based on individual needs and interacts with employees in
real-time, providing guidance. |
Challenges in Implementing Agentic Process Automation
While APA
offers exciting possibilities, it also comes with unique challenges. To ensure
that APA systems are beneficial and safe, companies need to address potential
issues around governance, security, and data privacy.
- Governance and Oversight: As APA systems become more
autonomous, organizations must establish strong governance frameworks to
oversee the actions and decisions of AI agents. Guardrails should ensure
that APA systems align with company policies and ethical standards.
- Data Privacy and Security: APA agents often require
access to large datasets to function effectively, which raises concerns
around data privacy. Companies must implement stringent security measures
to protect sensitive data and comply with regulatory standards.
- Ethical Concerns: APA systems must be designed
to avoid biases and ensure fairness. Training AI agents to augment rather
than replace human intelligence can help mitigate ethical concerns and
support a balanced automation strategy.
The Future of APA in the Workplace
APA
represents the next level in the evolution of digital workers, transforming
them from rule-following bots to intelligent agents capable of understanding
complex information and executing tasks autonomously. However, as APA adoption
grows, organizations should balance automation with human oversight to prevent
unintended consequences and maintain accountability.
Future
workplaces will likely adopt a hybrid model where APA agents handle a wide
range of tasks, from routine operations to complex problem-solving. This model
can create a synergistic relationship between human and digital workers,
enhancing productivity, improving operational flexibility, and unlocking new
levels of innovation.
Getting Started with Agentic Process Automation
To
successfully integrate APA, companies should start with a solid automation
foundation. Here are a few steps to ensure a smooth transition:
- Identify Opportunities for APA:
Begin by
identifying tasks where RPA has limitations, such as processes that
require contextual understanding or dynamic decision-making.
- Establish Data Infrastructure:
Since APA
relies on large datasets, organizations need to ensure data is accessible,
secure, and compliant with privacy standards.
- Build Strong Governance: Implement governance policies
to manage and monitor APA systems. This will help balance automation
benefits with ethical and compliance requirements.
- Empower Human Workers: Position APA as a tool that
complements, rather than replaces, human capabilities. Training and
upskilling employees to work alongside AI agents will maximize the impact
of APA.
Conclusion
Agentic
Process Automation represents a significant leap forward in automation
technology, blending the efficiency of RPA with the intelligence of AI. While
RPA remains an effective solution for rules-based, repetitive tasks, APA’s
advanced capabilities are better suited for complex scenarios that require
context, adaptability, and decision-making.
By
adopting APA, organizations can achieve new levels of efficiency and
innovation, freeing human employees to focus on strategic, high-value work.
Although there are challenges, with the right preparation, APA can be
integrated into modern workflows, setting the stage for a more intelligent and
agile workplace.